
AI2RL Lab Thanksgiving Feast 🔗
November 27, 2024
On November 27th, our lab came together at Dr. Kim's home to celebrate Thanksgiving with a joyful potluck gathering. The table was overflowing with a wide variety of delicious dishes, including meat skewers, beef, sushi, bulgogi, potato pancakes, and homemade cookies!
We spent the day sharing laughter and stories, enjoying each other's company over amazing food. It was a wonderful opportunity to relax and recharge after a semester of hard work and dedication as a lab.

AI and Instructional Design Outreach Workshop 🔗
November 16, 2024
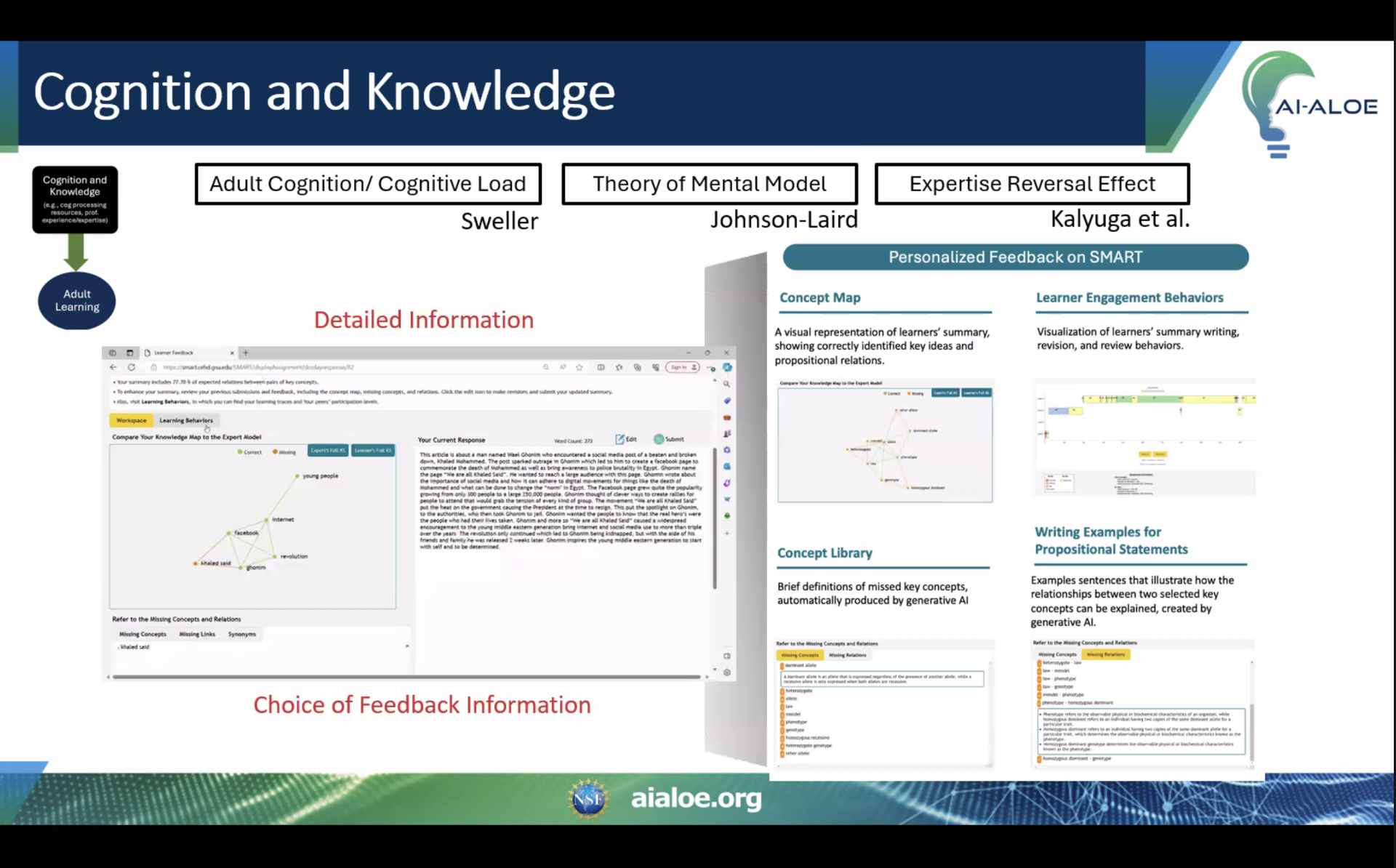
Dr. Min Kyu Kim and our graduate associates, Jinho Kim and Yoojin Bae, participated in AI-ALOE's AI and Instructional Design Outreach Workshop on November 15, 2024. This event served as a valuable opportunity to connect researchers and educators, emphasizing the intersection of AI innovation and instructional design practices. It also provided a platform to showcase the capabilities of our SMART technology.
Graduate associate Jinho Kim gave an insightful presentation on AI and personalized feedback, focusing on SMART. The presentation included an overview of SMART, its foundational theories, and associated research, demonstrating its potential to support personalized learning. Following the presentation, Dr. Min Kyu Kim led an engaging discussion to explore ideas and strategies for effectively integrating these tools into educational environments.
For more details about the workshop, check out these posts:
AI and Instructional Design Outreach Workshop

Exciting News: NSF-IUSE Project Featured in Research & Innovation! 🔗
November 9, 2024
Congratulations!
Our NSF-IUSE Project was highlighted in the Fall ’24 issue of Research & Innovation, and the story was also posted on the Georgia State News Hub.
Please see the full article in the link: LINK

Dr. Min Kyu Kim Joins AERJ Editorial Board 🔗
October 28, 2024
We are pleased to announce that our Founding Director, Dr. Min Kyu Kim, has been appointed as a member of the Editorial Board for the American Educational Research Journal (AERJ). AERJ is recognized as one of the most prestigious journals in the field of education. Congratulations to Dr. Kim on this well-deserved achievement!
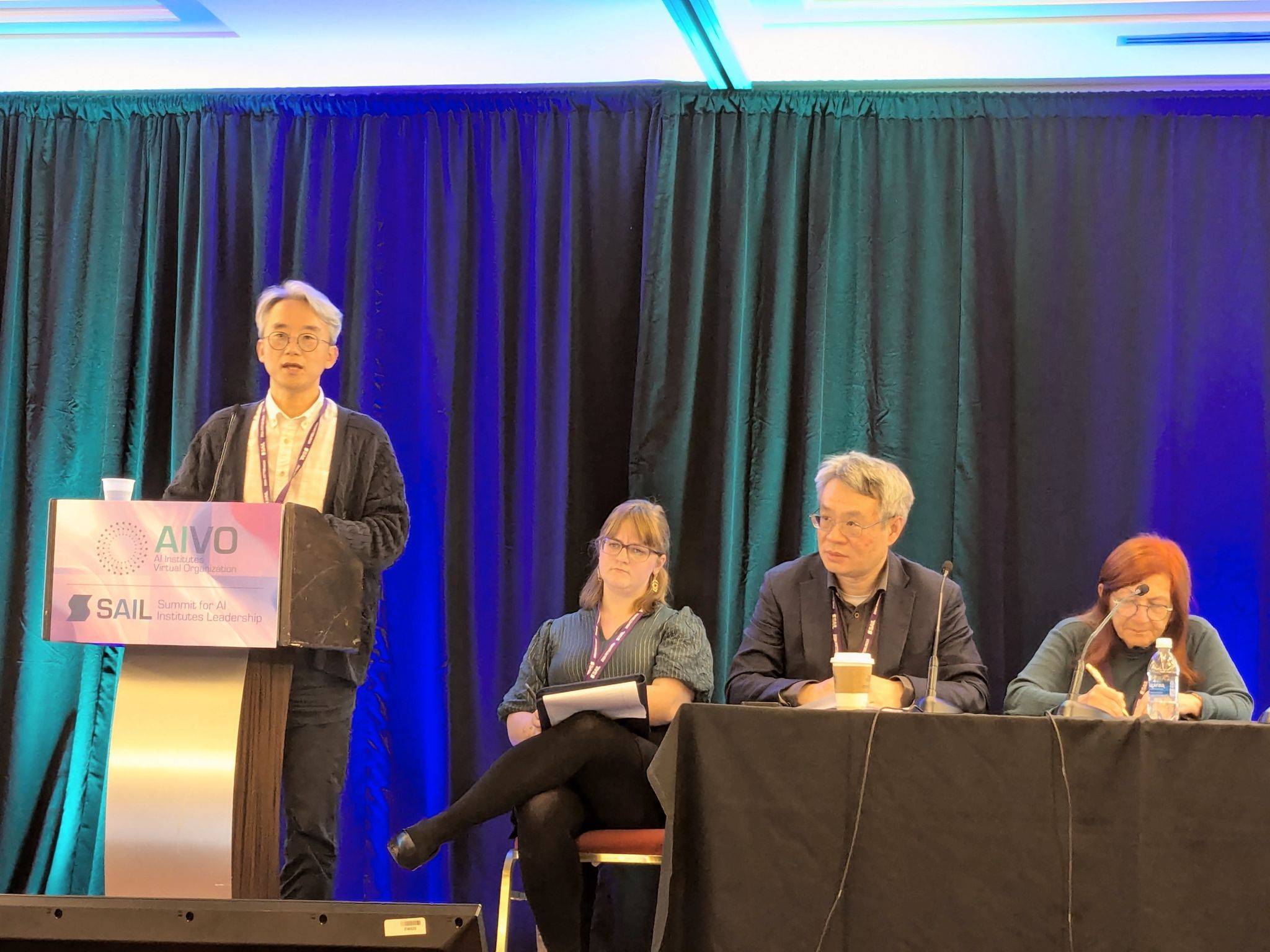

Dr. Min Kyu Kim Represents ALOE at Summit for AI Institutes Leadership (SAIL) in Pittsburgh. 🔗
October 10, 2024
From October 7 to October 10, Dr. Min Kyu Kim, attended the Summit for AI Institutes Leadership in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania (SAIL 2024). The event brought together representatives from 27 AI institutes funded by the National Science Foundation to discuss advancements in various fields, including food security, public safety, education, and weather forecasting.
On October 8, Dr. Kim served on a panel discussing foundational AI research. He shared insights on ALOE’s strategic approach to overcoming challenges and building foundational models for personalized learning in adult education and online environments. The discussion emphasized use-inspired connections, exploring both opportunities and obstacles in developing foundational AI models across various domains.
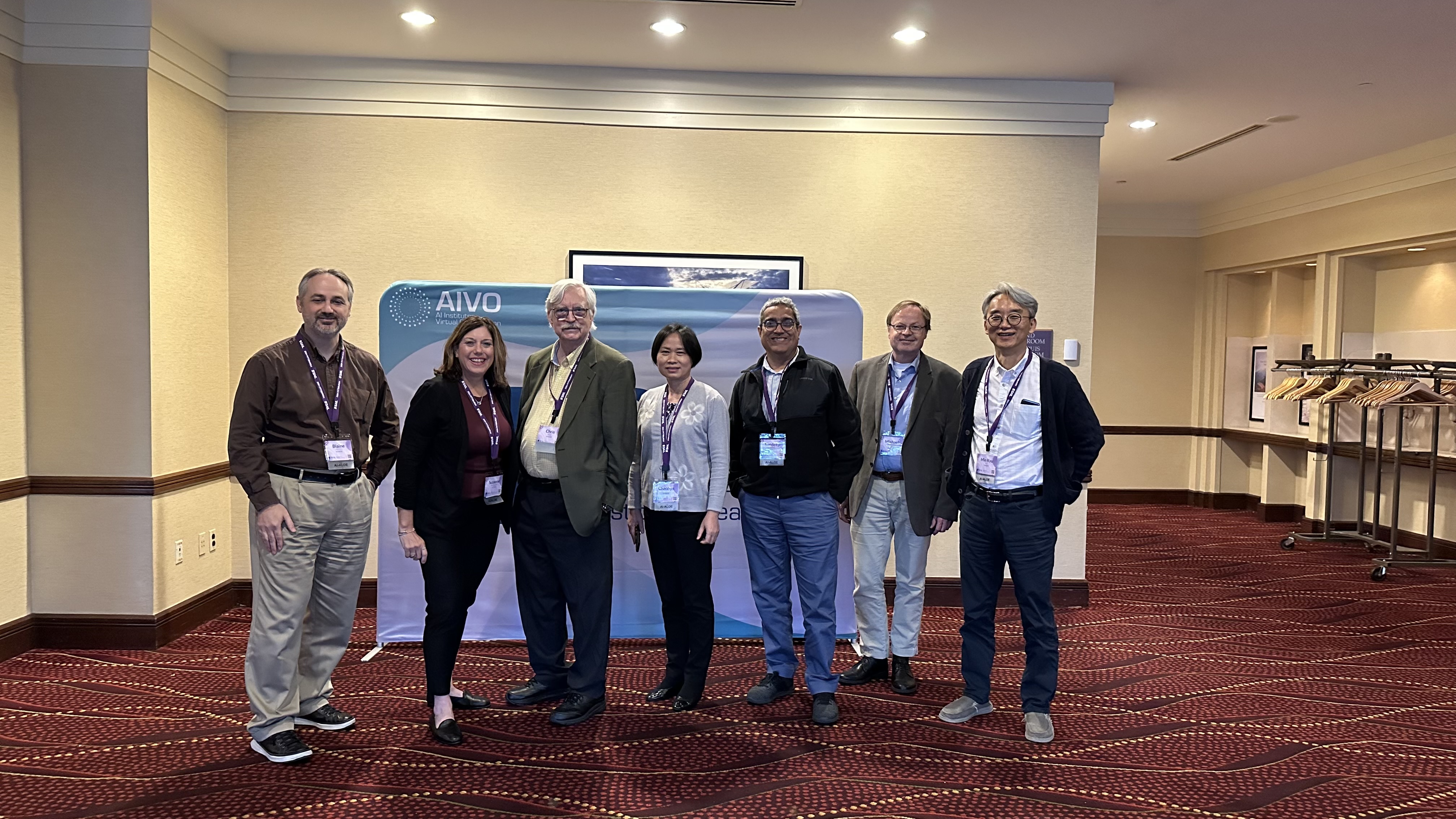


On October 10, Dr. Kim, along with the AI-ALOE team, participated in the AI Institutes Expo Day, where we shared with visitors how we develop and implement responsible AI to transform education and explored opportunities for collaboration. We had the pleasure of engaging in meaningful conversations with many attendees. We would like to thank the AI Institutes Virtual Organization (AIVO) for organizing and facilitating both the hashtag#SAIL2024 event and the Expo Day, two wonderful occasions that brought all the AI institutes together and connected us with the public.
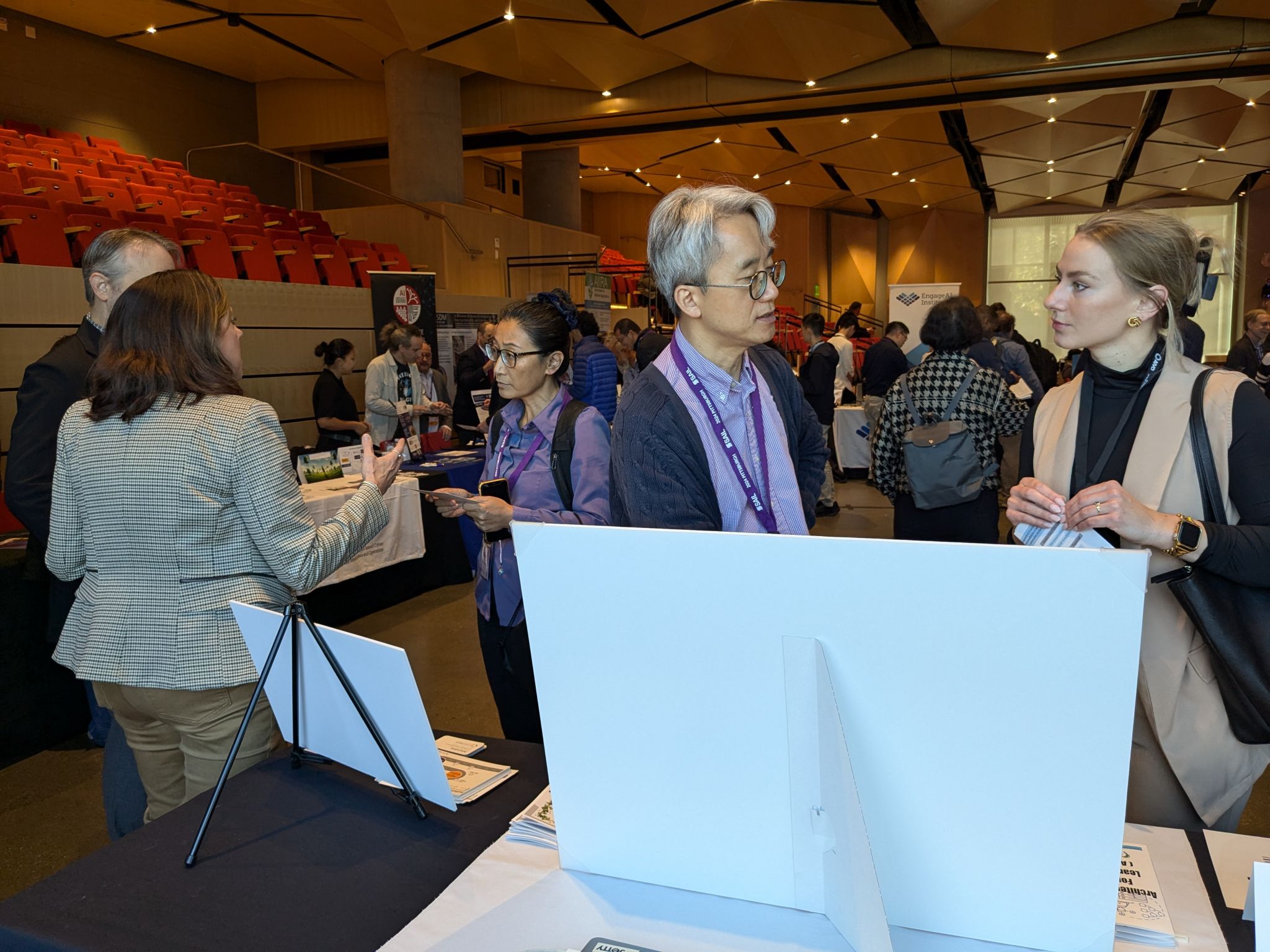
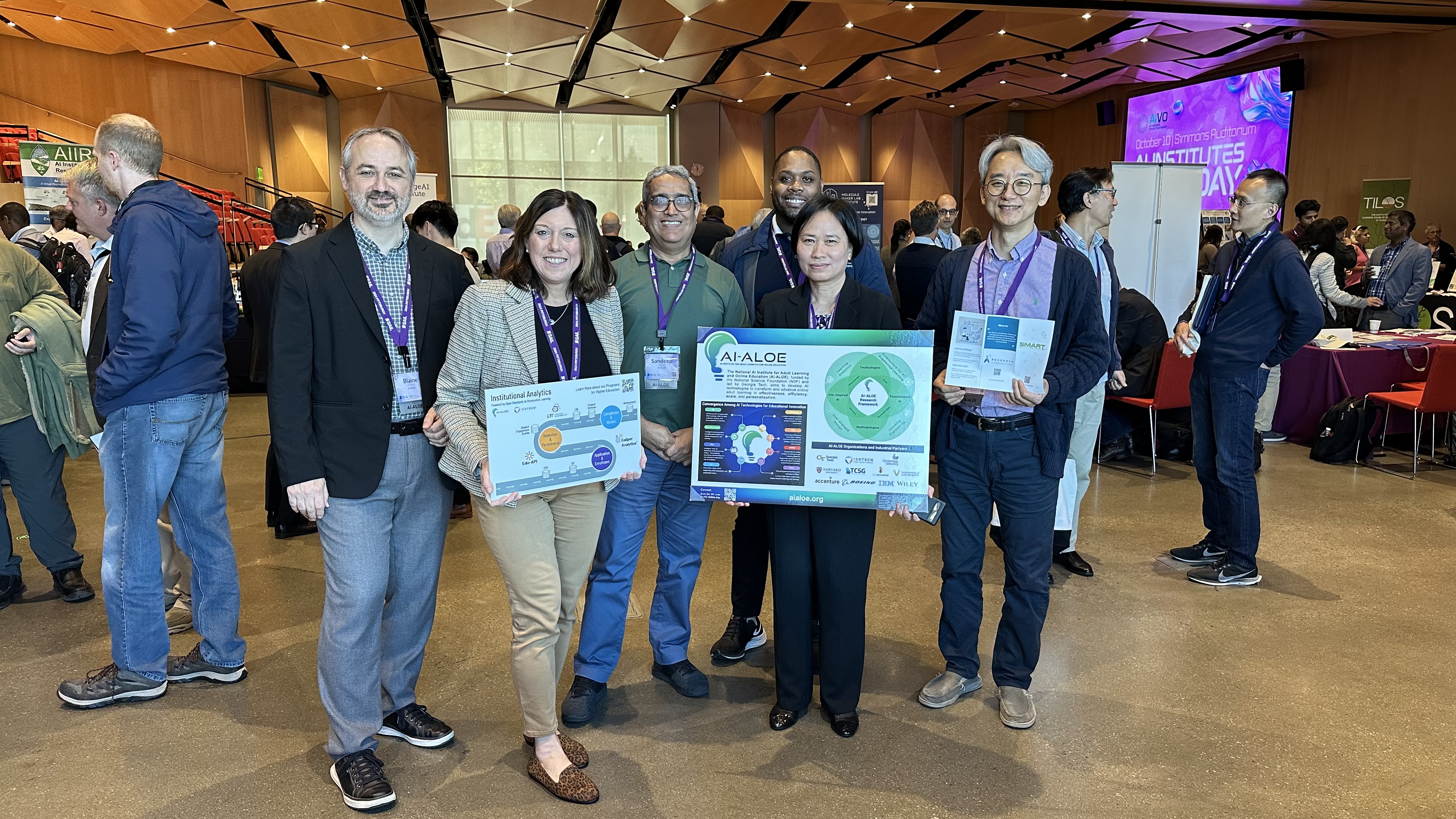




AI-ALOE Mini-Retreat: We presented SMART Research in Year 4 🔗
October 4, 2024
On October 2, 2024, our graduate associates, Jinho Kim, Seora Kim, Yoojin Bae, along with Dr. Min Kyu Kim attended AI-ALOE Mini-Retreat. Yoojin Bae and Seora Kim presented “SMART Research for Year 4,” focusing on technology integration in adult online education. Discussions centered on four key areas: educational goals for adult learners, instructional design collaboration, grounding in learning theories, and research contributions to adult education.
The retreat also showcased participatory instructional design and pilot programs, including the use of AI-augmented tools such as SMART to enhance learning experiences and support online education. The research aims to advance the field of adult learning through innovative AI applications.


Welcoming Seora Kim as a graduate research associate 🔗
August 26, 2024
We are happy to welcome Seora Kim as a new graduate research associate!
Seora Kim is a Graduate Research Associate and a Ph.D. student at the Department of Learning Sciences in the College of Education and Human Development, Georgia State University (GSU). She earned her Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) in Education and English language and literature, and Master of Arts (M.A.) in Education from Yonsei University, South Korea. Her research interests include educational technology, artificial intelligence-assisted learning to enhance critical thinking and creativity.

LT PhD Welcome (Back) Party 🔗
August 24, 2024
Happy New Academic Year 2024-2025!
We kicked off the new semester with our Learning Technology Welcome (Back) Party on August 24th!
The event was held at Wood's Chapel BBQ, where faculty members, graduate students, and their families gathered for a fun-filled afternoon of games, greetings, and camaraderie. With around 20 attendees, it was a wonderful opportunity to catch up with old friends and welcome new faces. We all had a fantastic time reconnecting and starting the academic year on a positive note!

Kicking Off Happickle Fridays 🔗
August 23, 2024
We kicked off our weekly Pickleball activity, "Happickle," on August 23rd at the Student Recreation Center! Our lab members gathered for a fun session of Pickleball, and it was a fantastic experience. Our visiting scholar and great coach, Sua, taught us step-by-step—from how to grip the pickleball paddle, to the basics of hitting the ball, and finally, to playing doubles games. Even the more complex rules were explained clearly and easily. A big thank you to Sua for her excellent coaching!
We’re also excited to unveil our new logo, created by our talented graduate associate, Seora :)
We plan to meet every Friday throughout the semester, so come join us for some fun and games!
Find out more on our Instagram page: @happickle_gsu!

Lia's recent achievements. Congratulations!! 🔗
August 15, 2024
Congratulations on Lia's (our graduate associate) recent achievements. Lia has earned many accolades this time, including a manuscript publication, an accepted conference presentation, and appointment as the Africa and Middle East Regional Representative for the International Learning Sciences Student Association (ILSSA) at ISLS/ICLS. Please refer to the details below.
Construction and Validation of a Computerized Formative Assessment Literacy (CFAL) Questionnaire for Language Teachers: An Exploratory Sequential Mixed-methods Investigation
Lia Haddadian has recently published a study to develop and validate a Computerized Formative Assessment Literacy (CFAL) questionnaire targeted toward language teachers. Recognizing the need for valid and reliable instruments to measure teachers’ literacy in Computerized Formative Assessment (CFA), the study adopted an exploratory sequential mixed-methods design drawing on a dual deductive-inductive approach. A total of 489 English as a Foreign Language (EFL) teachers participated, ranging from elementary to advanced levels, in eight major cities across Iran. Through Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA), this research identified six key factors, including practical, theoretical, socio-affective, critical, identity-related, and developmental. The research findings offer valuable insights and present significant implications for the development of professional programs aimed at assessing and enhancing teachers’ CFAL. These programs are essential for ensuring that teachers are well-equipped to leverage CFA effectively, ultimately improving both teaching practices and student learning outcomes.
Keywords: assessment, assessment literacy, formative assessment, formative assessment literacy, computerized assessment, computerized assessment literacy, literacy instruments, assessment literacy instruments
Haddadian, G., Radmanesh, S., & Haddadian, N. (2024). Construction and validation of a Computerized Formative Assessment Literacy (CFAL) questionnaire for language teachers: An exploratory sequential mixed-methods investigation. Language Testing in Asia, 14(33). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40468-024-00303-2
The Impact of AI-Enabled Personalized Recommendations on L2 Learners' Engagement, Motivation, and Learning Outcomes
Lia Haddadian will be presenting at the Teachers College, Columbia University, during the 2024 Artificial Intelligence Research in Applied Linguists (AIRiAL) Conference. The paper reports on two studies that investigated the effects of AI-enabled personalized recommendations on the engagement, motivation, and learning outcomes of L2 learners. Study 1 involved 50 intermediate students (17 males and 33 females) learning English as a second language, while study 2 involved another cohort of 50 participants (27 males and 23 females). Quasi-experimental design with repeated measures was conducted over six weeks. The experimental group received feedback from ChatGPT (GPT-4), while the control group received feedback from human tutors. In study 2, participants received feedback from both ChatGPT and their tutors. The findings indicated no statistically significant differences in learning outcomes between the experimental and control groups. Also, learners preferred AI-generated and human-generated feedback almost equally, with each type offering distinct benefits. There were no statistically significant differences in learning outcomes between the experimental and control groups, suggesting that AI-generated feedback for second language learning can be just as useful as feedback created by humans. Findings suggest that AI-generated feedback may be integrated into L2 learning assessment without negatively compromising learning outcomes, and that it can supplement human input to improve the learning experience.
Keywords: AI-enabled personalized recommendations, L2 learners, engagement, motivation, learning outcomes, generative AI tools.
Daneshvar, B., Haddadian, G. (Accepted). The Impact of AI-Enabled Personalized Recommendations on L2 Learners’ Engagement, Motivation, and Learning Outcomes. In 2nd Annual Artificial Intelligence Research in Applied Linguists (AIRiAL-2024) Conference, Teachers College, Columbia University: NY.
Appointment
Lia Haddadian has been appointed as the Africa and Middle East Regional Representative for the International Learning Sciences Student Association (ILSSA) at ISLS/ICLS. Congratulations to Lia Haddadian on this appointment!