
NSF IUSE-Engaged Student Learning (Level 1): AI-Scaffolded Pre-Classroom Learning for Large/Introductory Undergraduate Physics Courses
Budget: $ 298,375. Award period: 08/01/2023 – 07/31/2026
This Engaged Student Learning Level 1 project aims to serve the national interest by designing and implementing an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-augmented formative assessment and feedback system. This system will help students develop source-based STEM arguments, such as STEM text summarization, or problem spaces, which are mental representations of a problem and of multiple paths to solving it. This will be implemented in large, undergraduate introductory physics courses at an urban university that serves diverse and historically underrepresented student groups. Persistent learner engagement in pre-classroom learning activities is critical to learner success in introductory STEM courses. The innovation of the project will include AI-generated adaptive scaffolding information and learning progress feedback with data visualization techniques to help students with concept learning and self-regulatory behaviors. The unique learning opportunities supported by an AI-scaffolded feedback system will significantly increase students' engagement levels in self-paced online pre-classroom learning. This, in turn, will help students acquire content knowledge and build a proper understanding of problems to prepare themselves for success in in-classroom interactive problem-solving activities.
Budget: $ 19,990,448. Award period: 11/01/2021 – 10/31/2026
The ALOE institute is led by the Georgia Research Alliance (GRA), headquartered at Georgia Tech. The interdisciplinary and cross-institutional effort unites experts in computer science, artificial intelligence (AI), cognitive science, learning science and education from two Non-Profit Organizations (GRA and IMI Global), three industry partners (IBM, Boeing and Wiley) and seven universities (Georgia Tech, Georgia State, Harvard, Arizona State, Drexel, University of North Carolina, and multiple colleges within the Technical College System of Georgia [TCSG]). The multinational company Accenture joins NSF as a funding partner of ALOE.
The 5-year NSF grant is to establish the NSF AI Institute for Adult Learning and Online Education (ALOE) that will develop new AI theories and techniques as well as new models of lifelong learning, and evaluate their effectiveness at Georgia Tech, Georgia State, multiple colleges within the Technical College System of Georgia (TCSG), as well as with corporate partners IBM, Boeing and Wiley. ALOE aims to integrate AI theories, models, and techniques into online adult learning to create more available, affordable, adaptable, and scalable learning experiences, which creates more effective and efficient teaching and learning.
Budget: $ 399,681. Award period: 06/15/2021 – 05/31/2024
This project is to develop instructional modules and hands-on labs for a new course called “Private AI,” which teaches students to use certain techniques to address various privacy challenges in AI systems. They are also creating manuals to help teachers integrate the modules into their curriculum.
“Most students who take AI-related courses and security and privacy-related course are not familiar with the security and privacy issues of AI systems. Consequently, they may develop and deploy AI systems that are not trustworthy,” Kim said. “To resolve this issue, the project aims to develop instructional materials that make students naturally exposed to learning privacy issues of AI systems with real-world examples.”

How People Develop Learning Leadership: Learner Characteristics, Leadership Styles, and the Dynamics of Asynchronous Online Learning (Grant/Award Number: 201900017), Spencer Foundation.
Budget: $ 49,618. Award period: 07/01/2018 – 12/30/2019
Given the pervasive use of online learning in higher education, collaborative learning and peer-moderated learning are common strategies in online discussion. However, little is known about the way students learn "together" and take on leadership roles in their critical conversations. This project will take a data-analytics approach to describe and predict how people develop learning leadership and influence each other in online learning communities.
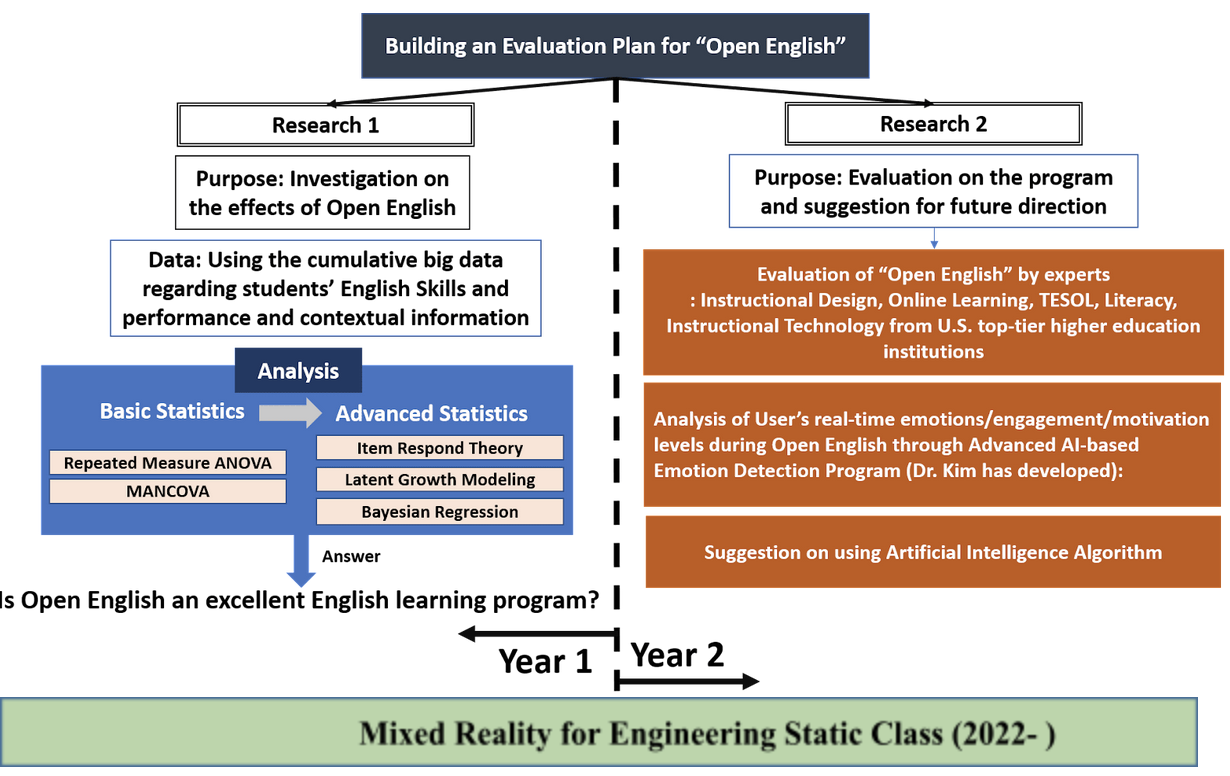
Big data analysis for Online English Learning Platform (2021 - 2023)
It is a multi-year evaluation project to investigate the effects of Open English (openenglish.com), which is drawing attention due to the provision of differentiated content according to the different learning targets and state-of-the-art teaching and learning platform, is suggesting directions for the ideal online English learning as the leader. For example, through the learning data analysis, recommendation, and reward system, a personalized program is recommended to the learner according to the learner's learning type or level. Also, Open English's 1:1 online tutoring is a learning method that dramatically improved English-speaking ability, which was considered a limitation in other online English learning methods.
.png)
Mini-Grants: Scholarship of Teaching & Learning (SoTL) (2021 – 2022)
Research in the science of learning suggests that active, generative writing tasks like summarization and explanation can support deeper comprehension and greater retention of complex text materials. Unfortunately, students do not receive many opportunities to engage in open-ended writing tasks in their content courses. This is in large part because evaluating open-ended tasks is time consuming and resource-intensive. To address this issue, this work uses two new AI-based systems: Student Mental Model Analyzer for Research and Teaching (SMART; Kim et al., 2016, 2020), designed to support study summary writing and AI Scaffolded Expository Argumentation (AISS, Kim et al., under review), designed to support student explanation writing. Both tools use natural language processing to analyze students’ responses and to provide immediate, individualized feedback. The project has two broad aims. The first is to examine the extent to which two content-based writing and revising activities – summarization and explanation -- can support students’ comprehension of complex course readings. The second is to explore how students’ respond to automated writing support in their content-classes.
_System.png)
Artificial Intelligence-Augmented Motivation Indicator (AIMI) System
AIMI is an AI-augmented system that detects learners’ real-time motivation levels. AIMI utilizes neural network algorithms that interpret student facial expressions to indicate students’ current emotions (i.e., anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, surprise, and neutral) and motivation levels in real-time.

SMART (Student Mental Model Analyzer for Research and Teaching) System
SMART is a formative assessment and feedback system that analyze students’ academic essays (e.g., summaries of a text) and provide feedback to help learners to build a solid knowledge structure of a complex problem situation or reading materials. SMART analyzes students’ mental models in three dimensions (surface, structure, and semantic).
AISS (Artificial Intelligence-Supported Scaffolding) System
AISS is a web-based system that helps students write evidence-supported expository essays. AISS provides scaffolding (e.g., text completion examples as expert models) that supports students to improve information literacy, argumentation skills, and writing skills in compliance with an academic writing style.
Learner Participation Profiles (LPP)
Students taking virtual courses are often asked to participate in online discussion forums – spaces where they can exchange their ideas and develop new knowledge and skills in a particular subject area.
To better understand students’ interactions in these online discussion settings, we developed and tested the computational model called Learner Participation Profiles that feature three different kinds of learners: Full, inbound and peripheral participants. Full participants moderate conversations and interact frequently with their peers via online messaging, while inbound participants work toward becoming more active by asking questions and providing thoughtful feedback. Peripheral participants, who are typically new to online collaborative learning, are more likely to take on an observational role and selectively participate in online conversations.
.png)
Leader Identification Method (LIM)
An asynchronous online discussion forum has been a prevalent means of collaborative online learning. Yet, it remains challenging for instructors to identify who and how students emerge as learning leaders. To overcome this challenge, we take a computational approach to identify learning leaders automatically. The Leader Identification Method (LIM) assumes that learning leaders emerge from social interactions in online discussions. The LIM conceptualizes three learning leadership roles: full facilitator, transactional facilitator, and attractive facilitator. These leadership roles are assumed to be associated with learners’ levels of engagement in behavior, cognition, and emotions.
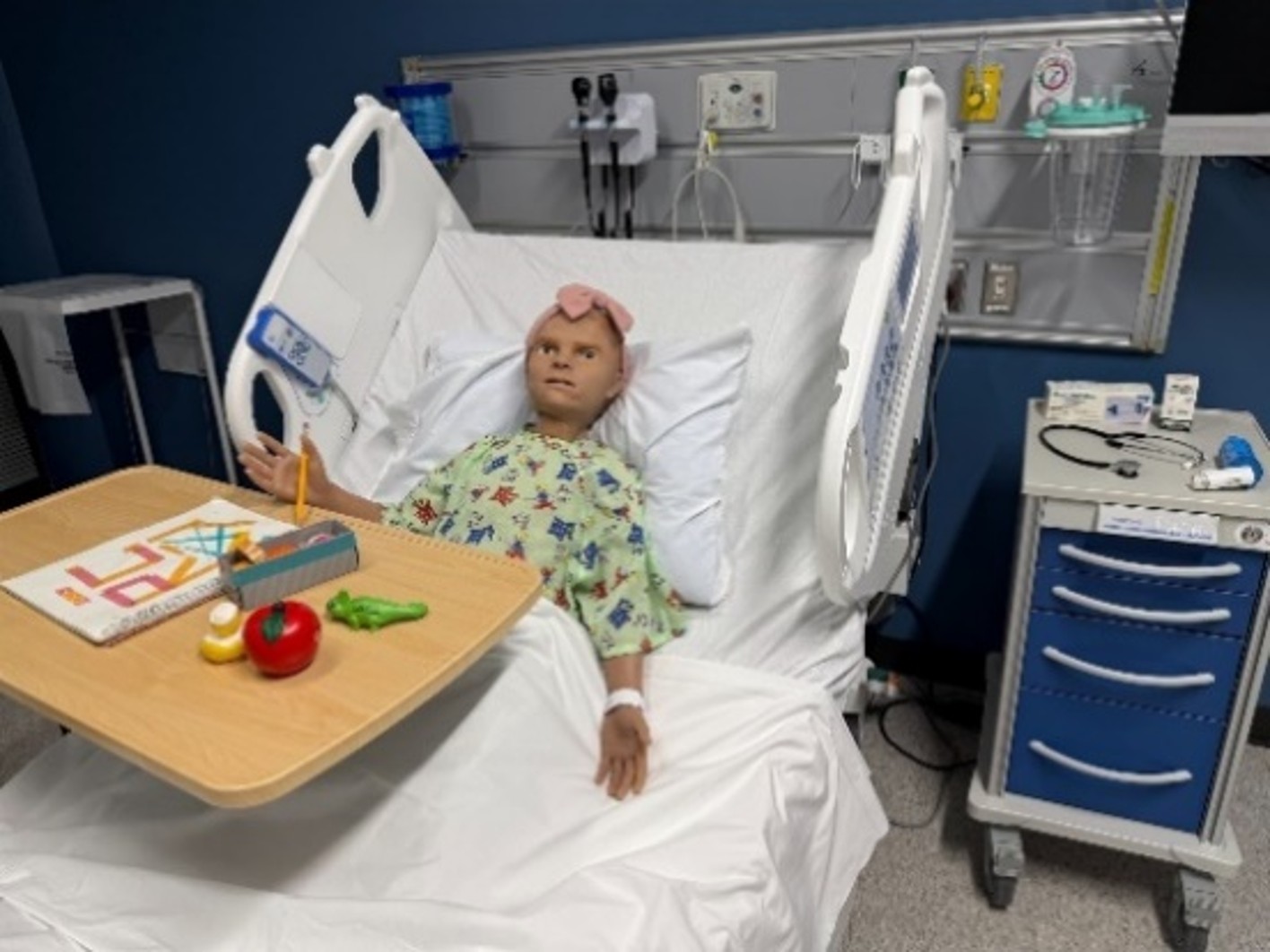
Scenario-Based Simulation Framework (S2F)
Fall 2024 -
Simulation-based learning plays an important role in nursing education but often faces challenges due to being resource-intensive, which limits accessibility and scalability. The S2F project, in collaboration with the School of Nursing at Georgia State University, aims to establish a flexible framework for facilitating simulation-based learning through a conversational AI-augmented simulator. This framework will provide instructors the flexibility to easily add scenario cases along with related assessment criteria. These scenarios will support learners in practicing simulations within physical simulation rooms as part of their nursing education, with assessments drawn from both dialogue interactions and visual data within the simulation space. The system will provide personalized feedback, supporting both simulation centers and individual practice. By leveraging the capabilities of AI and structured framework design, the project enables learners to continuously practice and refine critical thinking and communication skills in a realistic, flexible, and authentic environment.

Mixed Reality for Engineering Static Class (2022-2023)
This project is an interdisciplinary effort involving learning sciences and engineering to develop the pilot version of Augmented Reality module to cover three weeks’ contents of a static course through the systematic instructional model. Mixed methods research will investigate the impacts of AR-based Statics on (1) improvement of students' content-specific knowledge related to the abstract Statics concept, (2) enhancement of motivation toward engineering learning, and (3) reduce their cognitive overload.
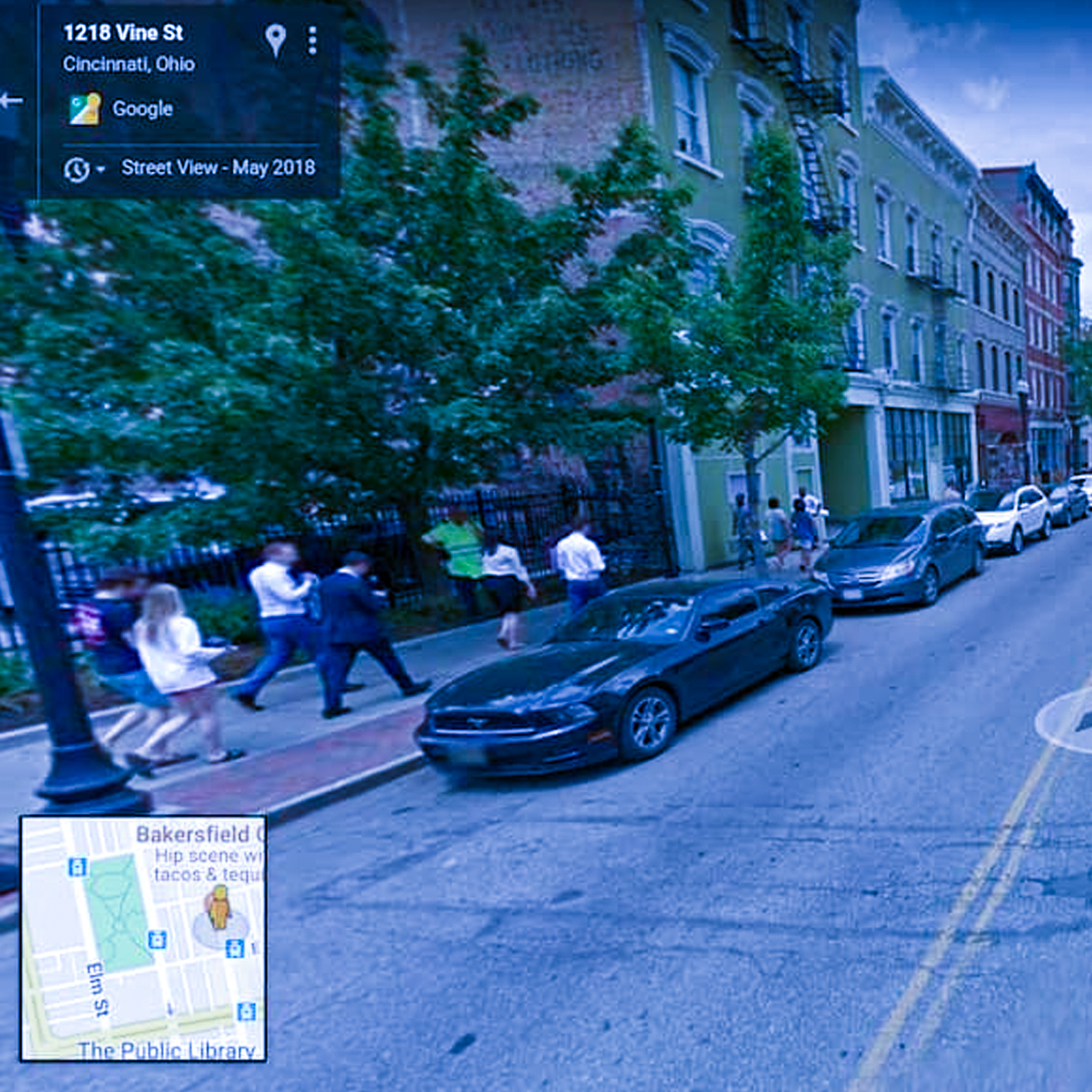
Read it More (2016- 2023)
RIM is a web-based instructional tool that helps students gain information literacy while engaging in a virtual field trip to collect real data on air quality from different locations. In RIM, students (a) are presented with an ill-structured/authentic problem that allows them to devise multiple solutions to bad air quality in their local city (b) can read an air quality vocabulary list and air quality study guide, and (c) engage with an animated tutorial (‘HeLIOS') that helps identify which information students need to find and find the information. After accomplishing the basic steps, students started to explore air quality across cities in a Virtual Field Trip (VFT). VFT provided real-world environments of several cities using ‘Google street view’, and students in VFT could explore and analyze the surrounding topography, related facilities, and natural environments of the place where they chose and walked around.


.png)